Resistors 1,225,090+ Parts
Resistor Category Description
Resistors are essential basic components in electronic circuits, which realize various circuit functions by controlling current and voltage. Dasenic provides the following types of resistors and related products: chassis mount resistors, chip resistors and surface mount resistors, special resistors, through-hole resistors and resistor network & array solutions.
Resistor Definition
Resistor is one of the most basic and common passive components in electronic circuits, used to limit current, divide voltage and adjust the resistance of the circuit. Resistors consume current by converting electrical energy into heat energy, thereby achieving control of current and voltage.
Structure of Resistor
The basic structure of a resistor includes a resistive material (such as carbon film, metal film or wire wound material) and two pins. The properties and geometric dimensions of the resistive material determine the resistance value of the resistor.
Classification of Resistors
Fixed Resistors: Resistors with fixed resistance values that cannot be adjusted. Widely used in all circuits to control current and voltage.
Variable Resistors: Resistors with adjustable resistance values, including potentiometers and adjustable resistors. Used to adjust voltage, current and signal strength in circuits.
Thermistor (NTC/PTC): A resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. Used in temperature sensors and overheat protection circuits.
Photoresistor: A resistor whose resistance changes with light intensity. Used in light sensors and light-operated switches.
Varistor (VDR): A resistor whose resistance changes with applied voltage. Used in overvoltage protection, lightning protection, etc.
Power resistor: A resistor that can withstand high power. Used in power supply circuits, load testing, etc.
Resistor identification
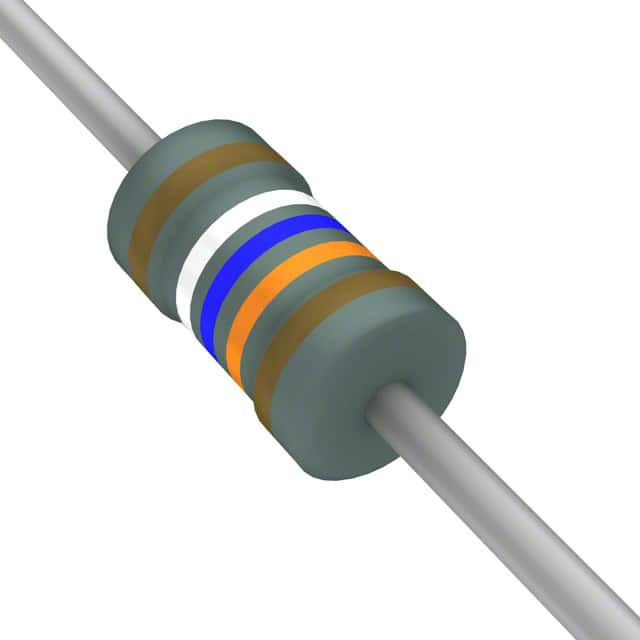
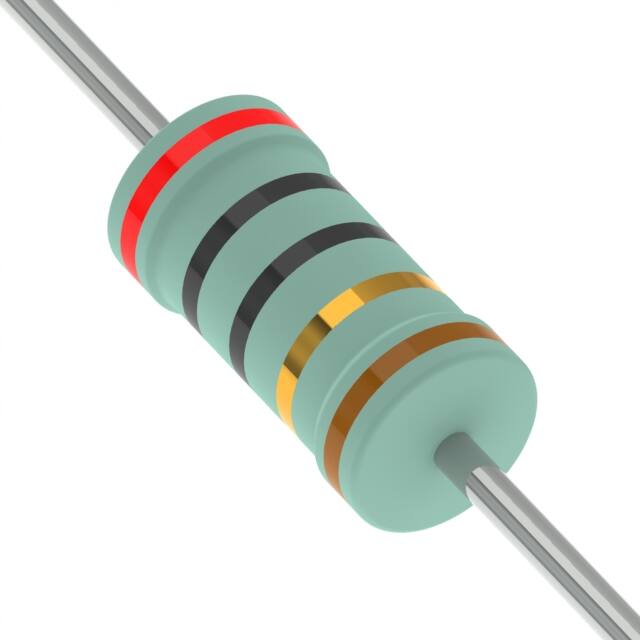
Resistors usually indicate their resistance directly through color rings, digital codes, or text.
Color ring identification: Commonly found in small resistors, the resistance value is indicated by a series of colored rings. The standard four-ring color code is as follows:
The first and second rings: indicate the first two digits of the resistance value.
The third ring: indicates the multiplication factor.
The fourth ring: indicates the tolerance (error range).
Digital coding: Some chip resistors use three or four digits to represent the resistance value, for example:
"103" means 10 × 10³ Ω = 10 kΩ.
They play a key role in power control, signal processing, temperature detection, etc. Choosing the right resistor requires considering its resistance value, tolerance, power rating, and application scenario to ensure the normal operation and reliability of the circuit.
Resistors Subcategories
Certified Manufacturers
KYOCERA AVX
144 Products
Analog Devices Inc.
92 Products
Analog Devices Inc./Maxim Integrated
59 Products
Bourns
688 Products
Caddock Electronics
336 Products
Cal-Chip Electronics
4895 Products
Cyntec
482 Products
ENAPROS INDIA
1 Products
Galco Industrial Electronics
8 Products
Gearbox Labs
1 Products
Honeywell
32 Products
Kamaya Inc.
1551 Products
KEMET
1 Products
Keystone Electronics
1 Products
KOA Speer Electronics, Inc.
734 Products
Littelfuse
8 Products
Meritek
9849 Products
Micro-Measurements
4 Products
Murata Power Solutions, Inc.
13 Products
NextGen Components, Inc.
29 Products
NTE Electronics Inc.
1788 Products
Ohmite
11278 Products
Panasonic
3317 Products
Riedon
1339 Products
SETsafe | SETfuse
4 Products
Skenos Technologies
4 Products
Stackpole Electronics
17512 Products
Susumu
22026 Products
TT Electronics
32 Products
TTM Technologies
4 Products
TubeDepot
732 Products
CTS Corporation
986 Products
Venkel
2364 Products
Viking Tech
9 Products
Visaton
19 Products
Vishay
356656 Products
Vishay Foil Resistors (Division of Vishay Precision Group)
15837 Products
Vishay Huntington Electric Inc.
43 Products
Vitrohm
56 Products
WAGO Corporation
1 Products
Walsin Technology Corporation
4886 Products
Waldom Electronics
1271 Products
YAGEO
67260 Products
Würth Elektronik
37 Products
Macom®
8 Products
Microchip
1 Products
Rochester Electronics
2 Products
ROHM Semiconductor
8340 Products
Samsung Electro-Mechanics
7974 Products
TE Connectivity
10521 Products